Altace
By W. Osko. Charleston Southern. 2018.
In this example order altace 2.5mg with mastercard, the new variable is called hdm2 and its values have been added in Variable View before conducting any analyses generic altace 5 mg otc. The only difference in the Crosstabulation table is that the rows have been interchanged. The x-axis is a logarithmic scale because odds ratios are derived from logarithmic values. When a factor is coded as risk or protection, the effect size is the same because on a logarithmic scale the odds ratios are symmetrical on either side of the line of unity. Ways in which the direction of risk can be changed during the analysis are to recode the dependent variable so that the category for which risk is of interest is coded with a higher number than the reference category. Alternatively, when running a binary logistic regression, the reference category can be changed under ‘Categorical, Change Contrast’. If cases with one factor present also tend to have another factor present, the effects of both factors will be included in each odds ratio. Thus, each odd ratio will be artificially inflated with the effect of the associated exposure; that is, confounding will be present. Logistic regression is used to calculate the effects of risk factors as independent odds ratios with the effects of other confounders removed. If an unadjusted odds ratio were used to calculate the risk of disease in the presence of exposure to factor I, then in a bivariate analysis, groups 2 and 3 would be combined and compared with group 1. In binary logistic regression, the variables that affect the probability of the outcome are measured as odds ratios, which are called adjusted odds ratios. Logistic regression is primarily used to determine which explanatory variables inde- pendently predict the outcome, when the outcome is a binary variable. In linear regression, the values of the outcome variables are predicted form one or more explanatory variables (see Chapter 7). In logistic regression, since the outcome is binary, the probability of the outcome occurring is calculated based on the given values of the explanatory variables. Logistic regression is similar to the linear regression in that a regression equation can be used to predict the probability of an outcome occurring. However, the logistic regression equation is expressed in logarithmic terms (or logits) and therefore regression coeffi- cients must be converted to be interpreted. Although the explanatory variables or predictors in the model can be continuous or categorical variables, logistic regression is best suited to measure the effects of exposures or explanatory variables that are binary variables. Continuous variables can be included but logistic regression will produce an estimate of risk for each unit of measurement. Thus, the assumption that the risk effect is linear over each unit of the variable must be met and the relationship should not be curved or have a threshold value over which the effect occurs. Logistic regres- sion is not suitable for matched or paired data or for repeated measures because the measurements are not independent – in these situations, conditional logistic regression is used. In addition, variables that are alternative outcome variables because they are on the same pathway of development as the outcome variable must not be included as independent risk factors. A large sample size is usually required to support a reliable binary logistic regression model because a cell is generated for each unit of the variable. If three variables each with two levels are included in the analysis, for example, an outcome and two explanatory variables, the number of cells in the model will be 2 × 2 × 2, or eight cells. As with chi-square analyses, a general rule of thumb is that the number of cases in any one cell should be at least 10. When there are empty cells or cells with a small number of cases, estimates of risk can become unstable and unreliable. Using this method, variables are added to the model one at a time in order of the magnitude of the chi-square association, starting with the largest estimate. At each step, changes to the model can be examined to assess multicollinearity and instability in the model. If an a priori decision is made to include known confounders, these can be entered first into the logistic regression and the model built up from there. Alternatively, Risk statistics 301 confounders can be entered at the end of the model building sequence and only retained in the model if they change the size of the coefficients of the variables already in the model by more than 10%. At each step of adding a variable to the model, it is important to compare the P values, the standard errors and the odds ratios in the model from Block 1 of 1 with the values from the second model in Block 2 of 2. A standard error that increases by an impor- tant amount, say by more than 10% when another variable is added to the model, is an indication that the model has become less precise. In this situation, the model is less stable as a result of two or more variables having some degree of multicollinear- ity and thus sharing variation. This indicates that the variable added to the model is a good predictor of the outcome and explains some of the variance.
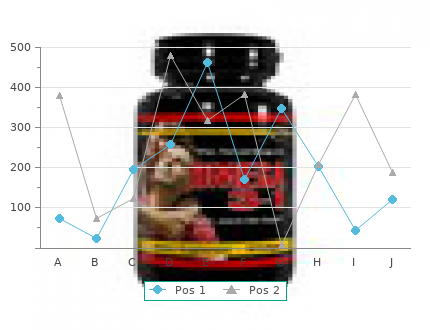
Between the two extremes of exploratory studies and confirmatory studies generic altace 2.5 mg without prescription, there is a wide range of different types of investigations − in all studies it is important to make a considered decision about what method buy altace 2.5 mg otc, if any, is used to control the type I error rate. The Multiple Comparisons table shows the mean difference between each pair of groups, the significance and the confidence intervals around the difference in means between groups. SigmaPlot can be used to plot the mean differences and 95% confi- dence intervals as a scatter plot with horizontal error bars using the commands shown in Box 3. This figure shows that three of the comparisons have error bars that cross the zero line of no difference. The remaining three comparisons do not cross the zero line of no difference and are statistically significant as indicated by the P values in the Multiple Comparisons table. Therefore, each P level obtained from a Bonferroni test in the Multiple Comparisons table should be evaluated at the critical level of 0. The mean values are identical but the confidence intervals are adjusted so that they are wider as shown in Figure 5. Under this test, there is a progressive comparison between the largest and smallest mean values until a difference that is not significant at the P < 0. The output from this test is presented as subsets of groups that are not significantly different from one another. Thus in the table, the mean values for groups of singletons and babies with one sibling are not significantly different from one another with a P value of 0. Similarly, the mean values of groups with one sibling, two siblings, or three or more siblings are not Homogeneous Subsets Weight (kg) Subset for alpha = 0. Singletons do not appear in the same subset as babies with two siblings or with three or more siblings which indicates that the mean weight of singletons is significantly different from these two groups at the P < 0. Means plot A means plot provides a visual presentation of the mean value for each group. It also provides visual evidence as to why the group with one sibling is not significantly different from singletons or babies with two siblings or with three or more siblings, and why singletons are significantly different from the groups with two siblings or with three or more siblings. Also, the line connecting the mean value of each group should be removed because the four groups are independent of one another. However, the cell sizes are unequal and therefore the weighted linear term is used. The table shows that the weighted linear term sum of squares is significant at the P = 0. The P value for the linear term-weighted indicates that the slope of the line through the plot is signifi- cantly different from zero. The descriptive statistics show that the mean weight increases as parity increases. When reporting the table, it is important to include details stating that weight was approxi- mately normally distributed in each group and that the group sizes were all large (min- imum 62) with a cell size ratio of 1:3 and a variance ratio of 1:1. The significant difference in weight at 1 month between children with different parities can be described as F = 3. The degrees of freedom are conventionally shown as the between-group and within-group degrees of freedom separated with a comma. If the Bonferroni post-hoc test had been conducted, it could be reported that the only significant difference in mean weights was between singletons and babies with two siblings (P = 0. If Duncan’s post-hoc test had been conducted, it could be reported that babies with two siblings and babies with three or more siblings were significantly different from singletons (P < 0. However, babies with one sibling did not have a mean weight that was significantly different from either singletons (P = 0. The term ‘uni- variate’ may seem confusing in this context but in this case refers to the fact that there is only one outcome variable rather than only one explanatory variable. The more explana- tory variables that are included in a model, the greater the likelihood of creating small or empty cells. The number of cells in a model is calculated by multiplying the number of groups in each factor. For a model with three factors that have three, two and four groups, respectively, as shown in Table 5. However, the between-group differences are again calculated as the difference of each participant from the grand mean, that is, the mean of the entire data set. When both random and fixed effect factors are included, this is referred to as a mixed model. A fixed factor is a factor in which all possible groups or all levels of the factor are included, for example, males and females or number of siblings. Usually, treatment effects such as a treatment group and a control group are fixed. With fixed factors, inferences can be made only to the levels of the factor used in the study. When using fixed factors, the differences between the specified groups are the statistics of interest.
See also Crohn’s dis- Crepitus in a joint can indicate cartilage wear in the ease order 10 mg altace visa. Crohn’s disease can be a chronic cheap altace 5mg overnight delivery, the formation of scar tissue (fibrosis) in the skin recurrent condition, or it can cause minimal symp- and sometimes also in other organs of the body. In more serious cases, deeper and larger Raynaud’s phenomenon (spasm of the tiny artery ulcers can develop, causing scarring, stiffness, and http://www. It is the bowel wall, leading to infection in the abdomi- usually caused by viruses but sometimes by bacte- nal cavity (peritonitis) and in adjacent organs. Symptoms include a cough that sounds like a Abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, fever, and seal’s bark and a harsh crowing sound during weight loss can be symptoms. Treatments concern with croup is difficulty breathing as the air include medications that reduce inflammation, sup- passages narrow. Dietary tration of moist air (as from a humidifier), saltwa- changes can reduce symptoms. Also known as regional suppressants, pain medication, fluids, and, if the enteritis. Crouzon syndrome A hereditary craniofacial Crohn’s ileitis Inflammation of the ileum (the disorder characterized by craniosynostosis, small lowest part of the small intestine) due to Crohn’s eye sockets that cause the eyes to protrude, a large disease. Some people with Crouzon syndrome also Crohn’s ileocolitis Crohn’s disease involving the have sleep apnea, hearing loss, and other difficul- ileum (the lowest portion of the small intestine) and ties. Crossing over is cryoglobulinemia The presence in blood of a way to recombine the genetic material so that each abnormal proteins called cryoglobulins that have person (except for identical twins) is genetically the unusual property of precipitating from the blood unique. Cryoglobulins can increase the risk of crossover study A type of clinical trial in which blood clots forming in the brain (stroke), eyes, and the study participants receive each treatment in a heart. With this type of study, every patient blood vessels (vasculitis), which increases the risk serves as his or her own control. Cryoglobulinemia can also are often used when researchers feel it would be accompany another disease, such as multiple difficult to recruit participants willing to risk going myeloma, dermatomyositis, or lymphoma. For example, the culdoscope The viewing tube (endoscope) technology of cooling and storing cells at a temper- introduced through the end of the vagina into the ature below the freezing point (–196° C) permits rectouterine pouch (the pouch of Douglas), an high rates of survivability of the cells upon thawing. Cultural evolution shows a rapid rate of crypt In anatomy, variously a blind alley, a tube change, is usually purposeful and often beneficial, is with no exit, a depression, or a pit in an otherwise widely disseminated by diverse means, is frequently fairly flat surface. For example, the tonsillar crypts transmitted in complex ways, and is enriched by the are little pitlike depressions in the tonsils. Cultural evolution is unique to humans among cryptorchidism A condition in which one or all forms of life. Any body tis- rected in early childhood are at increased risk for sue or fluid can be evaluated in the laboratory by developing cancer of the testicles. Also known as using culture techniques to detect and identify infec- undescended testicles. The word curette comes from French back that allows it to articulate posteriorly with the and means “scraper. It also has a joint in the front that permits it to articulate anteriorly with the Curie A unit of radioactivity. Specifically, a Curie fourth and fifth metatarsals (the bones just behind is the quantity of any radioactive nuclide in which the fourth and fifth toes). The term cul-de-sac is Cushingoid Having the constellation of symptoms used specifically to refer to the rectouterine pouch and signs seen in Cushing’s syndrome, caused by an (the pouch of Douglas), an extension of the peri- excess of cortisol hormone, particularly facial puffi- toneal cavity between the rectum and back wall of ness and unexplained weight gain. This cycle is governed by a complex sequence of hormones that influence fertility and Cushing’s syndrome A constellation of symp- may affect mood and a variety of physical functions. Cushing’s syndrome is a hormonal condition begin on the first day of menstrual bleeding. Cushing’s syndrome are due to the excess produc- tion of cortisol by the adrenal gland. It is important to tion (brand names: Neoral, Sandimmune) that is wash a cut with soap and water, and keep it clean prescribed chiefly for organ transplant recipients and dry, but avoid putting alcohol, hydrogen perox- and people with autoimmune disorders. Delay in getting medical care can increase the rate cyclothymia A form of bipolar disorder in which of wound infection. If a cut results from a puncture the mood swings are less severe than manic depres- wound through a shoe, there is a high risk of infec- sion. Redness, swelling, increased pain, and pus draining from the wound also indicate an infection cyst A closed sac or capsule, usually filled with that requires professional care. Also known as chalazion or cutaneous syndactyly See syndactyly, cuta- tarsal cyst. Still other types of ovarian cysts are called dermoid cysts, or ovarian cyanosis A bluish color of the skin and the teratomas. These bizarre but usually benign tumors mucous membranes due to insufficient oxygen in can contain many different body tissues, such as the blood. When a cyst causes symptoms, pain can be present at birth, as in a “blue baby,” an infant is by far the most common feature. Pain from an with a malformation of the heart that permits into ovarian cyst can be caused by rupture of the cyst, the arterial system blood that is not fully oxygenated. Treatment of ovarian cysts depends on the woman’s age, the size and type of the cyst, and the cycle, cell See cell cycle.
9 of 10 - Review by W. Osko
Votes: 131 votes
Total customer reviews: 131